A biometric authentication system verifies identities using unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris patterns. It enhances security and convenience by eliminating the need for passwords.
Biometric authentication systems are gaining popularity due to their high security and ease of use. These systems use unique biological traits, making them difficult to forge. Fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and iris patterns are common methods. They offer a seamless user experience and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Industries like banking, healthcare, and mobile security increasingly rely on biometrics. The technology ensures only authorized individuals gain access, enhancing data protection. As cyber threats evolve, biometric systems provide a robust solution, blending security with user convenience.
Introduction To Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication uses your unique features to verify your identity. These features include fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans. This method of security is becoming popular in various industries.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process. It uses your unique biological traits to verify who you are. This can include your fingerprint, face, or even your voice.
Evolution Of Biometric Systems
Biometric systems have evolved greatly over time. Early systems used simple methods like fingerprinting. Now, we have advanced technologies like facial and iris recognition.
Here is a brief timeline:
- 1858: First use of fingerprints for identification
- 1960s: Introduction of hand geometry systems
- 2000s: Facial and iris recognition become popular
- Present: Multimodal biometric systems are in use
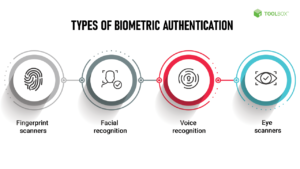
Types Of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication systems are transforming security. They use unique biological traits. Different types of biometric authentication provide various levels of security and convenience. Let’s explore some of the most common types.
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is one of the oldest and most common biometric methods. It scans the unique patterns of ridges on your fingertips. This method is widely used in smartphones and security systems.
- Highly accurate
- Fast and convenient
- Low cost
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology scans the unique features of your face. It uses advanced algorithms to map facial structures. This method is gaining popularity in airports and smartphones.
| Pros | Cons |
| Hands-free | Can be affected by lighting |
| Non-intrusive | Privacy concerns |
Iris Scanning
Iris scanning involves scanning the unique patterns in your iris. This method is highly accurate and difficult to spoof. It is used in high-security environments.
- High level of accuracy
- Requires specialized equipment
- Non-invasive
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition analyzes your voice patterns. It uses vocal characteristics to verify your identity. This method is convenient for remote authentication and phone systems.
- Easy to use
- Can be affected by background noise
- Useful for hands-free scenarios
How Biometric Authentication Works
Biometric Authentication is a secure method used to verify identity. It relies on unique biological characteristics. Here’s how biometric authentication works:
Data Collection
The process begins with data collection. This involves capturing a unique biological trait. Common traits include fingerprints, facial features, and iris patterns.
- Fingerprints are scanned using a fingerprint sensor.
- Facial features are captured via a camera.
- Iris patterns are recorded using an iris scanner.
Template Creation
Next, the system creates a template. This is a digital representation of the captured trait. The system uses complex algorithms to convert the data.
The template is stored securely in a database. It is a unique code that represents the biological trait.
Example:
Fingerprint data -> Algorithm -> Unique code template
Matching Process
The final step is the matching process. The system compares the new scan with the stored template. If they match, the identity is verified.
- User presents the biometric trait.
- System captures the data again.
- Data is converted to a digital template.
- System compares new template with stored one.
- If they match, access is granted.
Biometric authentication offers a high level of security. It is difficult to fake or steal biological traits. This makes it a popular choice for secure systems.
Advantages Of Biometric Systems
Biometric authentication systems offer several advantages. They enhance security and provide convenience. They also help in reducing fraud. Let’s explore these benefits in detail.
Enhanced Security
Biometric systems provide higher security than traditional methods. Passwords can be guessed or stolen. Biometric data is unique to each person. This makes it very hard to fake.
Common biometric methods include:
- Fingerprint recognition
- Facial recognition
- Voice recognition
- Iris scanning
These methods ensure only authorized users access sensitive information.
Convenience
Biometric systems are very convenient. You do not need to remember passwords or carry cards.
Here are some ways biometric systems are used:
- Unlocking phones
- Accessing bank accounts
- Entering secure buildings
Simply using your fingerprint or face makes the process quick and easy.
Reduced Fraud
Biometric systems reduce fraud significantly. Traditional methods can be easily bypassed. Biometric data is unique and hard to replicate.
Here is a comparison of traditional and biometric methods:
| Traditional Methods | Biometric Methods |
| Passwords | Fingerprint |
| PINs | Facial recognition |
| Security questions | Voice recognition |
Using biometrics greatly reduces the chances of fraud.
Challenges And Limitations
Biometric authentication systems offer many advantages. But they also come with challenges and limitations. These can affect their adoption and effectiveness. In this section, we will discuss these key issues.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns are significant in biometric systems. These systems collect and store personal data. This data includes fingerprints, facial features, and iris scans.
Hackers can target this sensitive information. If stolen, it can lead to identity theft. Biometric data is unique and cannot be changed. This makes the impact of a breach severe and long-lasting.
Users may also worry about misuse. Companies and governments could use biometric data for surveillance. This raises ethical and privacy issues.
Technical Issues
Biometric systems can face various technical issues. These issues can affect their performance and reliability.
For instance, false positives and false negatives can occur. A false positive means the system incorrectly grants access. A false negative means it denies access to an authorized user.
Environmental factors also play a role. Poor lighting or dirty sensors can cause errors. Technical failures may lead to system downtime. This can disrupt access and operations.
Cost Implications
Implementing biometric systems can be expensive. The initial setup cost is high. This includes purchasing hardware and software. Training staff to use the system also adds to the cost.
Maintenance is another factor. Keeping the system updated and secure requires ongoing investment. Smaller businesses may find these costs prohibitive. This can limit the widespread adoption of biometric systems.
| Challenge | Description |
| Privacy Concerns | Risk of data breaches and misuse |
| Technical Issues | False positives and negatives, environmental factors |
| Cost Implications | High initial and maintenance costs |
Applications In Various Industries
Biometric authentication systems are revolutionizing industries with their secure and efficient methods. These systems use unique biological traits for identification. Let’s explore how different sectors utilize this technology.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, biometric authentication ensures patient safety. It helps in avoiding medical identity theft. Doctors use it to access patient records quickly and securely. Biometric systems streamline patient check-ins. They also help in managing access to restricted areas.
Banking And Finance
Biometric authentication in banking and finance enhances security. It protects against fraud and unauthorized access. Customers use fingerprints to access accounts. Banks use facial recognition for secure online banking. This technology reduces the need for complex passwords. It also speeds up transactions.
Travel And Transportation
In travel and transportation, biometric systems simplify the boarding process. Airports use facial recognition for passenger identification. This reduces wait times and enhances security. Railways and buses use fingerprints for ticket verification. It ensures only valid passengers board.
Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics benefit greatly from biometric authentication. Smartphones use fingerprints and facial recognition for unlocking. This provides a higher level of security. Laptops and tablets also use biometrics for secure access. This technology ensures personal data remains safe.
Future Trends In Biometric Authentication
The future of biometric authentication is evolving rapidly. Innovations are shaping how we secure our digital identities. Let’s explore some key trends in biometric authentication that are driving this change.
Ai And Machine Learning Integration
AI and Machine Learning are enhancing biometric systems. These technologies improve accuracy and efficiency. They can analyze vast amounts of data quickly. AI can detect fraudulent activities in real-time. Machine learning adapts to new patterns and threats. This makes biometric systems smarter and more reliable.
Multimodal Biometric Systems
Multimodal biometric systems use more than one biometric trait. This increases security and reduces errors. Combining fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice can provide robust authentication. Multimodal systems are harder to spoof. They offer better accuracy and user experience.
Remote Biometric Verification
Remote biometric verification allows authentication from anywhere. Users can verify their identity using mobile devices. This is crucial for online banking and remote work. Remote verification ensures secure access without physical presence. It also supports contactless authentication, enhancing user convenience.
| Trend | Benefit |
| AI and Machine Learning | Improved accuracy and real-time fraud detection |
| Multimodal Systems | Enhanced security and reduced errors |
| Remote Verification | Convenient and secure remote access |
The future of biometric authentication promises enhanced security and user convenience. These trends are transforming how we protect digital identities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Example Of Biometric Authentication?
An example of biometric authentication is fingerprint scanning. It uses unique fingerprint patterns to verify identity. This method is commonly used in smartphones and secure access systems.
What Are The Two Types Of Biometric Authentication?
The two types of biometric authentication are physiological and behavioral. Physiological includes fingerprints and facial recognition. Behavioral includes voice and typing patterns.
How Do I Get Biometric Authentication?
Visit a biometric service center. Provide necessary documents and complete the registration process. Follow instructions for fingerprint or facial scan.
What Devices Use Biometric Authentication?
Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and security systems use biometric authentication. Other devices include smart locks, ATMs, and access control systems.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication uses unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial recognition to verify identity.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work?
It captures and compares biological data with stored templates to confirm identity.
Is Biometric Authentication Secure?
Yes, it’s generally more secure than traditional passwords due to unique biological traits.
What Are Examples Of Biometric Authentication?
Examples include fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and iris scanning.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication systems offer enhanced security and user convenience. They reduce fraud risks and streamline access control. As technology advances, biometric methods will become even more reliable. Investing in biometric systems can protect sensitive information and improve user experience. Stay ahead in security by adopting biometric authentication today.


3 Reply on “Groundbreaking Biometric Authentication System: Transforming Digital Security in 2024”